Your Synaptic response to an action potential images are ready. Synaptic response to an action potential are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Get the Synaptic response to an action potential files here. Find and Download all free vectors.
If you’re searching for synaptic response to an action potential pictures information connected with to the synaptic response to an action potential topic, you have visit the ideal site. Our site frequently gives you suggestions for refferencing the highest quality video and image content, please kindly search and locate more informative video content and images that fit your interests.
Synaptic Response To An Action Potential. The action potential moving down a myelinated axon will jump from one Node of Ranvier to the next. The transmitters then act on neurotransmitter receptors in the postsynaptic membrane. These chemicals are made by the cell that is sending the impulse the pre-synaptic neurone and stored in synaptic vesicles at the end of the axon. An action potential AP is the mode through which a neuron transports electrical signals.
 Chemical Transmission At The Synapse Pharmacology Nursing Human Anatomy And Physiology Medical Mnemonics From pinterest.com
Chemical Transmission At The Synapse Pharmacology Nursing Human Anatomy And Physiology Medical Mnemonics From pinterest.com
An action potential allows a nerve cell to transmit an electrical signal down the axon toward other cells. Chemical Synapse Neurotransmitter Release by Casey Henley is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial Share-Alike CC. Postsynaptic conductance changes and the potential changes that accompany them alter the probability that an action potential will be produced in the postsynaptic cell. Then sodium and potassium permeability properties of the neuronal plasma membrane as well as their changes in response to alterations in the membrane potential are used to convey the details of the. The response of a nerve or muscle cell to an action potential can vary according to how frequently and for what duration the action potentials are fired. An action potential is the result of a very rapid rise and fall in voltage across a cellular membrane with every action potential impulse similar in size.
Synapse sinaps the junction between the processes of two neurons or between a neuron and an effector organ where neural impulses are transmitted by chemical means.
The action potential travels down the neuron to the presynaptic axon terminal. An action potential occurs when a portion of the membrane rapidly depolarizes and then repolarizes again to the original resting state. The process is initiated by a threshold level stimulus such as a nearby change in membrane potential threshold potential local potential. The response of a nerve or muscle cell to an action potential can vary according to how frequently and for what duration the action potentials are fired. Temperature sensing in the POA has historically been attributed to the requisite and cell-autonomous role of WSNs ie neurons that increase action potential AP firing in response to temperature increase Madden and Morrison 2019. An action potential requires an.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Indeed the large amplitude of the EPP ensures that an action potential always is. Temperature sensing in the POA has historically been attributed to the requisite and cell-autonomous role of WSNs ie neurons that increase action potential AP firing in response to temperature increase Madden and Morrison 2019. Immune response to foreign. Synapse sinaps the junction between the processes of two neurons or between a neuron and an effector organ where neural impulses are transmitted by chemical means. Presynaptic boutons with a.
 Source: loretocollegebiology.weebly.com
Source: loretocollegebiology.weebly.com
An action potential cannot cross the synaptic cleft between neurones. Intracellular recordings can detect the smaller graded potential changes that serve to trigger action potentials. An action potential occurs when a portion of the membrane rapidly depolarizes and then repolarizes again to the original resting state. This saltatory conduction leads to faster propagation speeds than when no myelin in present. Through binding to postsynaptic receptors the neurotransmitter can cause excitatory or inhibitory postsynaptic potentials by depolarizing or hyperpolarizing respectively the.
 Source: nature.com
Source: nature.com
An action potential cannot cross the synaptic cleft between neurones. In neuroscience an excitatory postsynaptic potential EPSP is a postsynaptic potential that makes the postsynaptic neuron more likely to fire an action potentialThis temporary depolarization of postsynaptic membrane potential caused by the flow of positively charged ions into the postsynaptic cell is a result of opening ligand-gated ion channels. An action potential is generated in the body of the neuron and propagated through its axon. An action potential requires an. One form of excitable dendritic response is the backpropagating action potential.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Postsynaptic conductance changes and the potential changes that accompany them alter the probability that an action potential will be produced in the postsynaptic cell. You selected the Send Payment option for your registration. Both pre- and postsynaptic cells have membrane specializations 1. Synaptic vesicles neurotransmitter vesicles b. Active zones for dockingrelease of contents of vesicles 2.
 Source: oist.jp
Source: oist.jp
Indeed the large amplitude of the EPP ensures that an action potential always is. An action potential allows a nerve cell to transmit an electrical signal down the axon toward other cells. Postsynaptic potentials are changes in the membrane potential of the postsynaptic terminal of a chemical synapsePostsynaptic potentials are graded potentials and should not be confused with action potentials although their function is to initiate or inhibit action potentials. At the neuromuscular junction synaptic action increases the probability that an action potential will occur in the postsynaptic muscle cell. When the action potential reaches the synaptic terminal it causes the release of chemical neurotransmitter.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
The influx of Ca 2 causes neurotransmitter acetylcholine-containing vesicles to dock and fuse to the presynaptic neurons cell membrane. It is defined as a brief change in the voltage across the membrane due to the flow of certain ions into and out of the neuron. This saltatory conduction leads to faster propagation speeds than when no myelin in present. Role of Action Potential. An action potential occurs when a portion of the membrane rapidly depolarizes and then repolarizes again to the original resting state.
 Source: droualb.faculty.mjc.edu
Source: droualb.faculty.mjc.edu
Intracellular recordings can detect the smaller graded potential changes that serve to trigger action potentials. They are caused by the presynaptic neuron releasing neurotransmitters from the terminal bouton at the end of an axon. This sends a message to the muscles to provoke a response. Phases of the cardiac action potential can also be correlated with the ECG. Then sodium and potassium permeability properties of the neuronal plasma membrane as well as their changes in response to alterations in the membrane potential are used to convey the details of the.
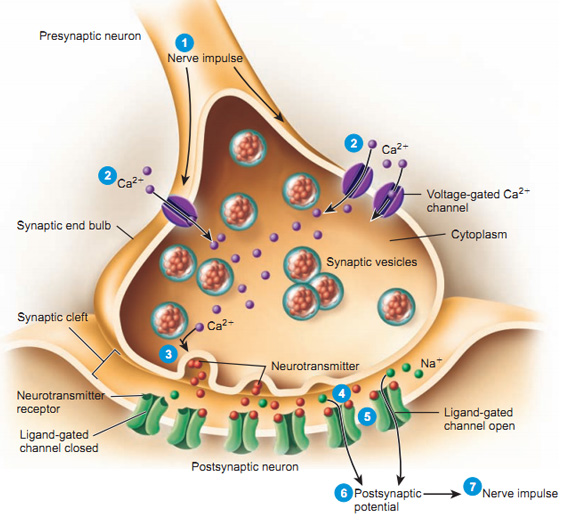 Source: teaching.ncl.ac.uk
Source: teaching.ncl.ac.uk
Short-term synaptic enhancement results from more synaptic terminals releasing transmitters in response to presynaptic action potentials. Postsynaptic conductance changes and the potential changes that accompany them alter the probability that an action potential will be produced in the postsynaptic cell. In a chemical synapse the action potential causes release of neurotransmitter molecules into the synaptic cleft. These chemicals are made by the cell that is sending the impulse the pre-synaptic neurone and stored in synaptic vesicles at the end of the axon. Following its initiation in the axon the action potential propagates into the dendrites of the pyramidal neuron though with some decrement in amplitude as it propagates Stuart et al 1997.
 Source: doctorlib.info
Source: doctorlib.info
An action potential occurs when a portion of the membrane rapidly depolarizes and then repolarizes again to the original resting state. One form of excitable dendritic response is the backpropagating action potential. 4 At the motor end plate the action potential causes the release of packets or quanta of acetylcholine into the synaptic clefts on the surface of the muscle fiber. Intracellular recordings can detect the smaller graded potential changes that serve to trigger action potentials. An action potential is generated in the body of the neuron and propagated through its axon.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Role of Action Potential. 4 At the motor end plate the action potential causes the release of packets or quanta of acetylcholine into the synaptic clefts on the surface of the muscle fiber. The lecture starts by describing the electrical properties of non-excitable cells as well as excitable cells such as neurons. The action potential moving down a myelinated axon will jump from one Node of Ranvier to the next. An action potential cannot cross the synaptic cleft between neurones.
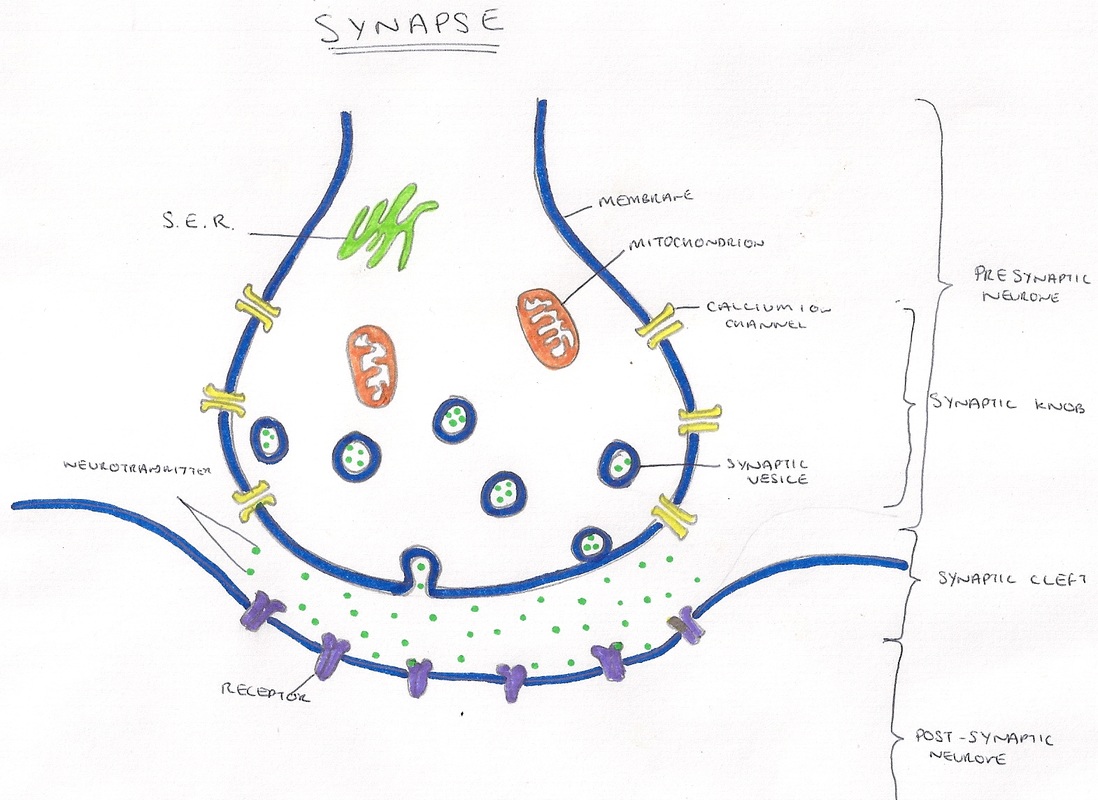 Source: alevelbiologystudent.weebly.com
Source: alevelbiologystudent.weebly.com
An action potential requires an. Voltage-dependent calcium channels open and Ca 2 ions flow from the extracellular fluid into the presynaptic neurons cytosol. Postsynaptic conductance changes and the potential changes that accompany them alter the probability that an action potential will be produced in the postsynaptic cell. At the neuromuscular junction synaptic action increases the probability that an action potential will occur in the postsynaptic muscle cell. One form of excitable dendritic response is the backpropagating action potential.
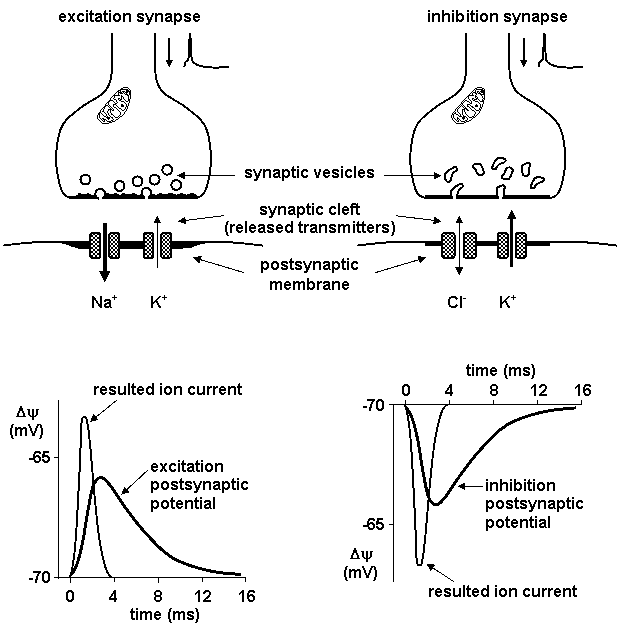 Source: www1.lf1.cuni.cz
Source: www1.lf1.cuni.cz
Both pre- and postsynaptic cells have membrane specializations 1. An action potential is the result of a very rapid rise and fall in voltage across a cellular membrane with every action potential impulse similar in size. Phase 0 and 1 are the QRS complex. This saltatory conduction leads to faster propagation speeds than when no myelin in present. Another form of dendritic excitability is the dendritically initiated.
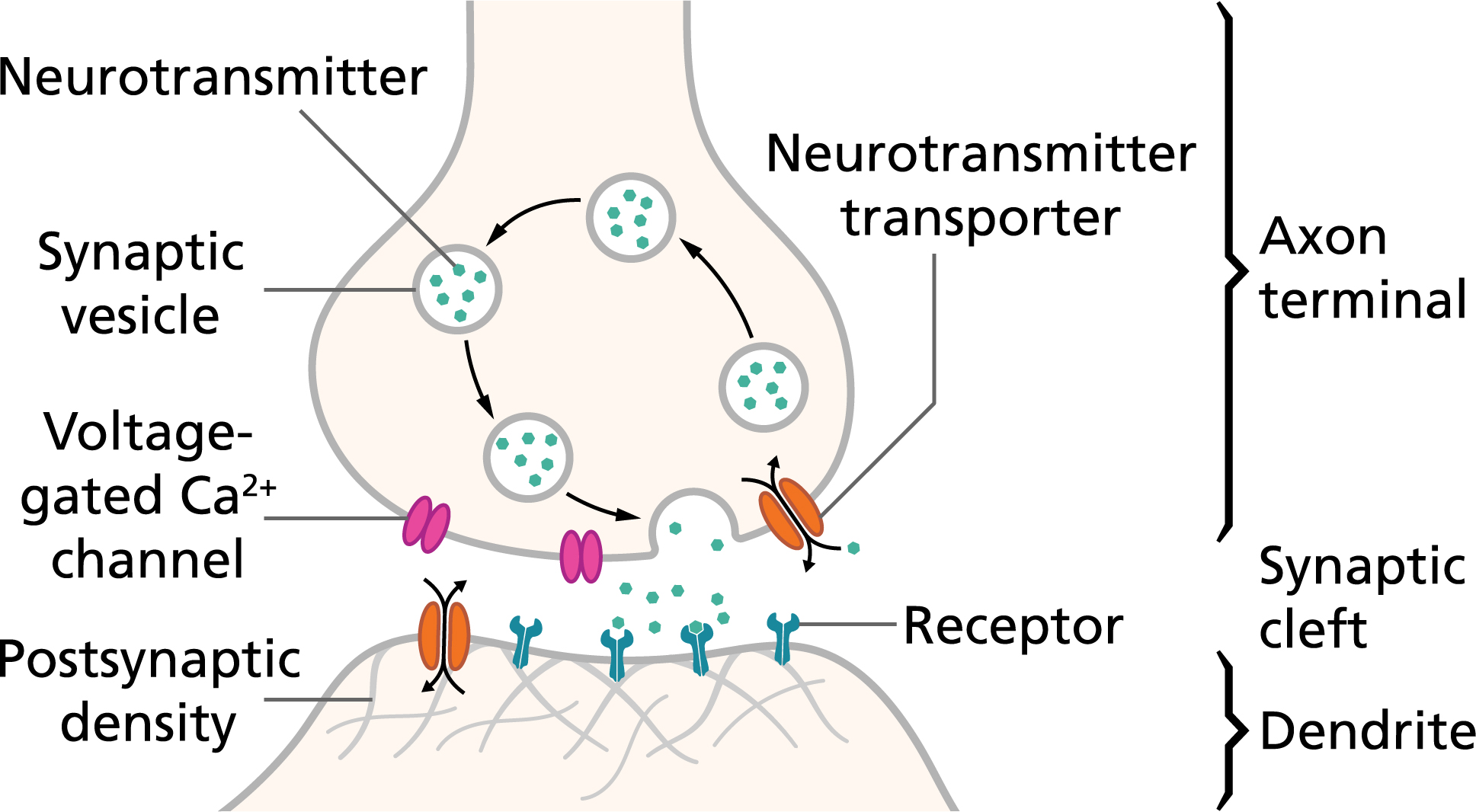 Source: qbi.uq.edu.au
Source: qbi.uq.edu.au
Indeed the large amplitude of the EPP ensures that an action potential always is. This lecture describes the details of the neuronal action potential. An action potential is the result of a very rapid rise and fall in voltage across a cellular membrane with every action potential impulse similar in size. Phases of the cardiac action potential can also be correlated with the ECG. Indeed the large amplitude of the EPP ensures that an action potential always is.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
The response of a nerve or muscle cell to an action potential can vary according to how frequently and for what duration the action potentials are fired. Short-term synaptic enhancement results from more synaptic terminals releasing transmitters in response to presynaptic action potentials. Indeed the large amplitude of the EPP ensures that an action potential always is. An action potential requires an. An action potential can be generated in different types of cells in the body facilitating their unique.
 Source: droualb.faculty.mjc.edu
Source: droualb.faculty.mjc.edu
An action potential AP is the mode through which a neuron transports electrical signals. They are caused by the presynaptic neuron releasing neurotransmitters from the terminal bouton at the end of an axon. An action potential is the result of a very rapid rise and fall in voltage across a cellular membrane with every action potential impulse similar in size. One form of excitable dendritic response is the backpropagating action potential. The transmitters then act on neurotransmitter receptors in the postsynaptic membrane.
 Source: getbodysmart.com
Source: getbodysmart.com
One form of excitable dendritic response is the backpropagating action potential. Phases of the cardiac action potential can also be correlated with the ECG. These graded triggering potentials can arise at either sensory receptors or synapses and are called receptor potentials or synaptic potentials respectively. Active zones for dockingrelease of contents of vesicles 2. Postsynaptic conductance changes and the potential changes that accompany them alter the probability that an action potential will be produced in the postsynaptic cell.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Another form of dendritic excitability is the dendritically initiated. These chemicals are made by the cell that is sending the impulse the pre-synaptic neurone and stored in synaptic vesicles at the end of the axon. Temperature sensing in the POA has historically been attributed to the requisite and cell-autonomous role of WSNs ie neurons that increase action potential AP firing in response to temperature increase Madden and Morrison 2019. Both pre- and postsynaptic cells have membrane specializations 1. The influx of Ca 2 causes neurotransmitter acetylcholine-containing vesicles to dock and fuse to the presynaptic neurons cell membrane.

Voltage-dependent calcium channels open and Ca 2 ions flow from the extracellular fluid into the presynaptic neurons cytosol. An action potential AP is the mode through which a neuron transports electrical signals. An action potential allows a nerve cell to transmit an electrical signal down the axon toward other cells. The impulse causes the release of a neurotransmitter eg acetylcholine or norepinephrine from the presynaptic membrane of the axon terminal. The neurotransmitter molecules diffuse.
This site is an open community for users to do submittion their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site value, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title synaptic response to an action potential by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






