Your Polymyxin mechanism of action images are available in this site. Polymyxin mechanism of action are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Find and Download the Polymyxin mechanism of action files here. Find and Download all free photos and vectors.
If you’re looking for polymyxin mechanism of action images information connected with to the polymyxin mechanism of action topic, you have visit the ideal site. Our website always gives you suggestions for downloading the maximum quality video and picture content, please kindly search and locate more informative video content and images that match your interests.
Polymyxin Mechanism Of Action. Both polymyxin B and colistin are rapid-acting bactericidal agents with a detergent-like mechanism of action. Mechanism of ActionPolymyxin B. This binding destroys bacterial membranes with a surface detergent-like mechanism resulting in increased cell membrane permeability and loss of essential metabolites. Proteus neisseria are resistant.
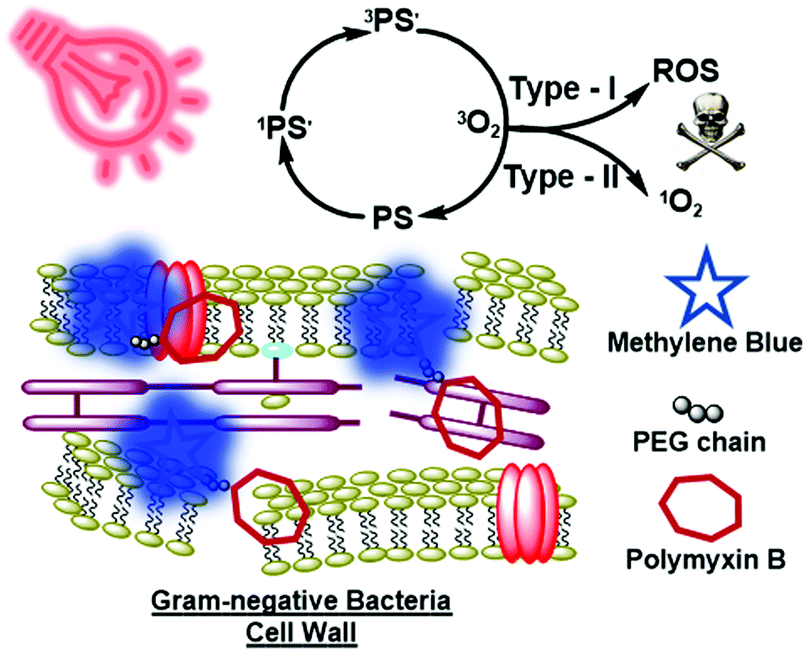 Polymyxin Based Photosensitizer For The Potent And Selective Killing Of Gram Negative Bacteria Chemical Communications Rsc Publishing Doi 10 1039 D0cc00155d From pubs.rsc.org
Polymyxin Based Photosensitizer For The Potent And Selective Killing Of Gram Negative Bacteria Chemical Communications Rsc Publishing Doi 10 1039 D0cc00155d From pubs.rsc.org
As a result of the structural similarity between colistin and polymyxin B it has been suggested that they share the same mechanisms of action 920. Antibiotic resistance among pathogenic bacteria is an ever-increasing issue worldwide. Neuromuscular blockade induced by polymyxins has been attributed to a presynaptic action through blockade of the release of acetylcholine into the synaptic gap 14. What is polymyxin btrimethoprim-ophthalmic and how does it work mechanism of action. Polymyxins are bactericidal with a time-dependent rate of killing at concentrations above their Minimal Bactericidal Concentration MBC. The mechanism of NDH-2 inhibition by polymyxin B was investigated in detail with Escherichia coli inner membrane preparations and conformed to.
This review focuses primarily on the proposed alternative mechanisms of action known resistance mechanisms and how these support the alternative mechanisms of.
Hydroxyl radical death mechanism in bacteria induced by polymyxin. The mechanism of NDH-2 inhibition by polymyxin B was investigated in detail with Escherichia coli inner membrane preparations and conformed to. Polymyxin B is a cationic polypeptide that binds the lipid-A portion of endotoxin. Both polymyxin B and colistin are rapid-acting bactericidal agents with a detergent-like mechanism of action. Polymyxin B is an antibiotic that disrupts the outer cell membrane of Gram negative bacteria binds and neutralizes lipopolysaccharide and inhibits respiration of Gram-negative bacterial cells 4. Then will be converted to H 2 O 2 by SOD superoxide dismutase.
 Source: europepmc.org
Source: europepmc.org
Inhibits bacterial cell wall synthesis by preventing the incorporation of amino acids and nucleotides into the cell wall. The exact antibacterial mechanism by which colistin can kill bacterial cells is not well understood. Causes leakage of bacterial membrane by binding to phospholipids Trimethoprim. 9 10 17 Polymyxins interact with lipopolysaccharide LPS of the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria and are subsequently taken up via the self-promoted uptake pathway. Antibiotic resistance among pathogenic bacteria is an ever-increasing issue worldwide.
 Source: pubs.rsc.org
Source: pubs.rsc.org
Proteus neisseria are resistant. Polymyxins are bactericidal with a time-dependent rate of killing at concentrations above their Minimal Bactericidal Concentration MBC. 9 10 17 Polymyxins interact with lipopolysaccharide LPS of the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria and are subsequently taken up via the self-promoted uptake pathway. Mechanisms of polymyxin activity against Gram-negative bacteria resistance. This can be noted first as fatiguability 126 hours after dosing and can progress to severe muscular weakness including respiratory paralysis 13.
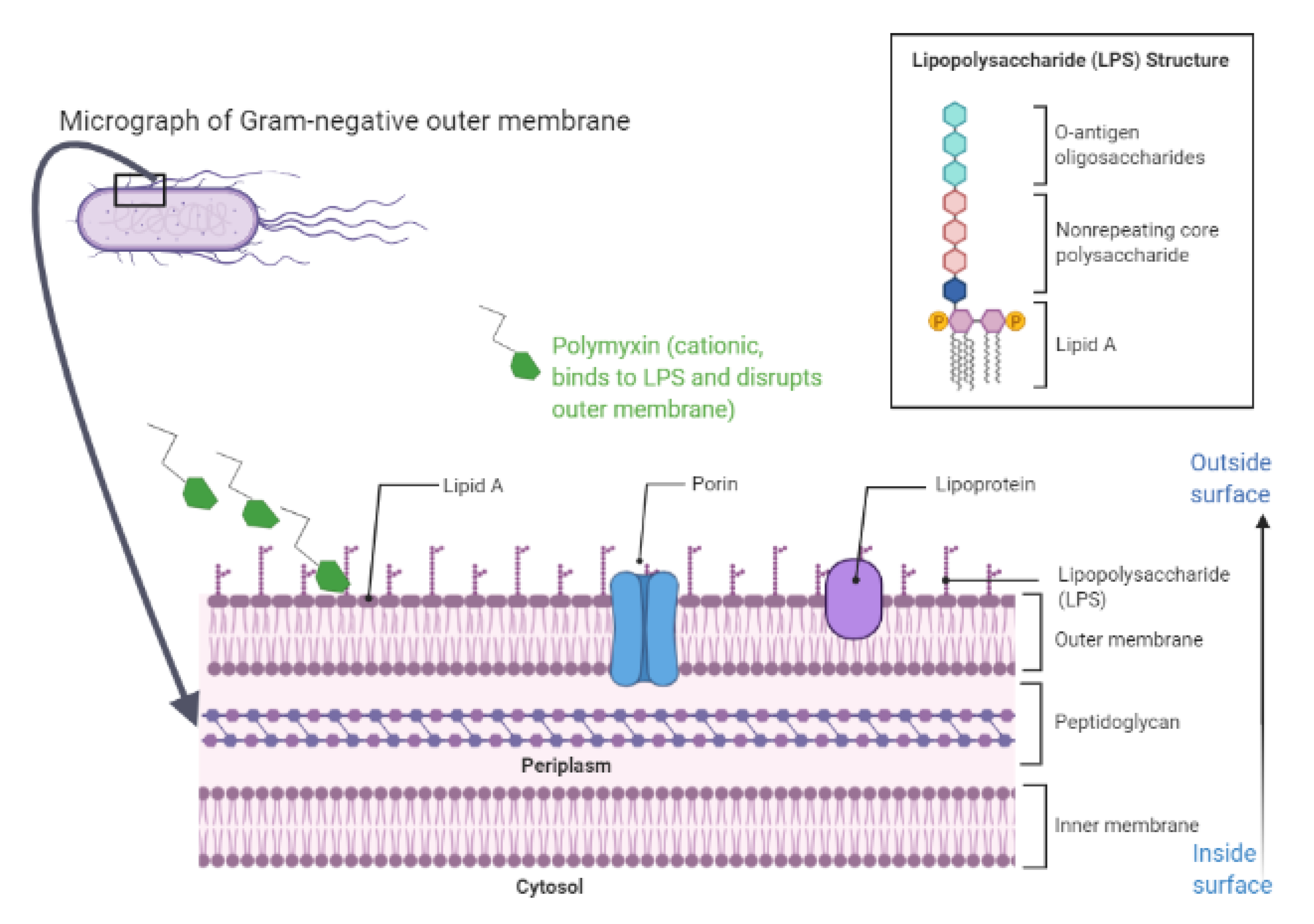 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
Polymyxin B sulfate works by altering bacterial cell wall structure that causes the leaking out. Mechanisms of polymyxin activity against Gram-negative bacteria resistance. Then will be converted to H 2 O 2 by SOD superoxide dismutase. Alternative Mechanisms of Action and Resistance. The exact antibacterial mechanism by which colistin can kill bacterial cells is not well understood.

Polymyxin B is a cationic polypeptide that binds the lipid-A portion of endotoxin. Polymyxin B can be given by a number of routes to treat susceptible Gram negative bacterial infections. Polymyxin B binds to phospholipids on cell membranes of gram-negative bacteria. As a result of the structural similarity between colistin and polymyxin B it has been suggested that they share the same mechanisms of action 920. Alternative Mechanisms of Action and Resistance.
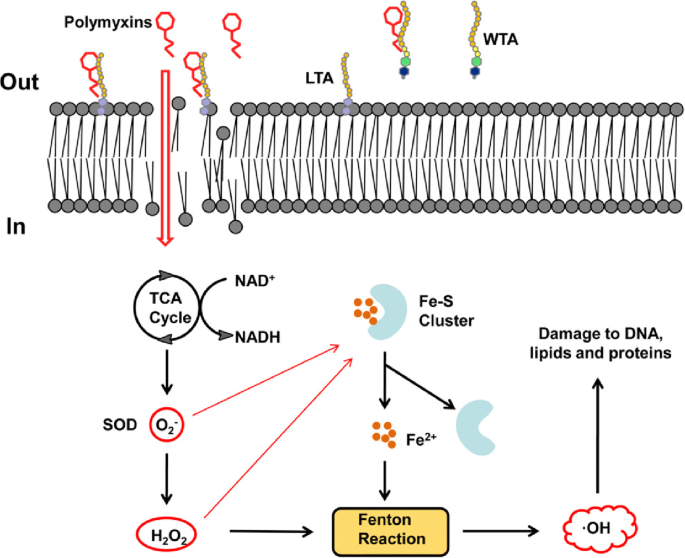 Source: link.springer.com
Source: link.springer.com
This can be noted first as fatiguability 126 hours after dosing and can progress to severe muscular weakness including respiratory paralysis 13. The hydrophobic tail is important in causing membrane damage suggesting a detergent-like mode of action. Causes leakage of bacterial membrane by binding to phospholipids Trimethoprim. The polymyxin molecule magenta comes across inner membrane IM and induces superoxide generation. It is on the World Health Organizations List of Essential Medicines the safest and most effective medicines needed in.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
Polymyxin B was approved for medical use in the United States in 1964. Newton 1956 originally sug-gested that the mechanism. Blocks production of tetrahydrofolic acid from dihydrofolic acid by binding to and reversibly inhibiting the enzyme dihydrofolate reductas. The hydrophobic tail is important in causing membrane damage suggesting a detergent-like mode of action. 9 10 17 Polymyxins interact with lipopolysaccharide LPS of the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria and are subsequently taken up via the self-promoted uptake pathway.
 Source: pubs.rsc.org
Source: pubs.rsc.org
It is on the World Health Organizations List of Essential Medicines the safest and most effective medicines needed in. Polymyxin B can be given by a number of routes to treat susceptible Gram negative bacterial infections. The mechanism of NDH-2 inhibition by polymyxin B was investigated in detail with Escherichia coli inner membrane preparations and conformed to. In addition to affecting gram-negative bacteria they bind to inactivate endotoxin LPS. What is polymyxin btrimethoprim-ophthalmic and how does it work mechanism of action.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Both polymyxin B and colistin are rapid-acting bactericidal agents with a detergent-like mechanism of action. Antibiotic resistance among pathogenic bacteria is an ever-increasing issue worldwide. Polymyxin B sulfate works by altering bacterial cell wall structure that causes the leaking out. Both polymyxin B and colistin are rapid-acting bactericidal agents with a detergent-like mechanism of action. Proteus neisseria are resistant.

19 The polycationic peptide ring binds to the outer membrane displacing the calcium. Polymyxins are bactericidal with a time-dependent rate of killing at concentrations above their Minimal Bactericidal Concentration MBC. In addition to affecting gram-negative bacteria they bind to inactivate endotoxin LPS. 19 The polycationic peptide ring binds to the outer membrane displacing the calcium. This review focuses primarily on the proposed alternative mechanisms of action known resistance mechanisms and how these support the alternative mechanisms of.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Polymyxin B sulfate trimethoprim is an antibiotic eye drop composed of two drugs. Hydroxyl radical death mechanism in bacteria induced by polymyxin. Polymyxin B was approved for medical use in the United States in 1964. The polymyxin molecule magenta comes across inner membrane IM and induces superoxide generation. Mechanisms of polymyxin activity against Gram-negative bacteria resistance.
 Source: cell.com
Source: cell.com
Polymyxin B works by breaking down the cytoplasmic membrane which generally results in bacterial cell death. Polymyxin B can be given by a number of routes. Polymyxin B sulfate works by altering bacterial cell wall structure that causes the leaking out. Unfortunately very little has been achieved in the pharmaceutical industry to combat this problem. 19 The polycationic peptide ring binds to the outer membrane displacing the calcium.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Polymyxin B is an antibiotic that disrupts the outer cell membrane of Gram negative bacteria binds and neutralizes lipopolysaccharide and inhibits respiration of Gram-negative bacterial cells 4. Blocks production of tetrahydrofolic acid from dihydrofolic acid by binding to and reversibly inhibiting the enzyme dihydrofolate reductas. Polymyxin B is an antibiotic that disrupts the outer cell membrane of Gram negative bacteria binds and neutralizes lipopolysaccharide and inhibits respiration of Gram-negative bacterial cells 4. Alternative Mechanisms of Action and Resistance. The hydrophobic tail is important in causing membrane damage suggesting a detergent-like mode of action.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Polymyxin B is an antibiotic that disrupts the outer cell membrane of Gram negative bacteria binds and neutralizes lipopolysaccharide and inhibits respiration of Gram-negative bacterial cells. The mechanism of NDH-2 inhibition by polymyxin B was investigated in detail with Escherichia coli inner membrane preparations and conformed to. Mechanism of action. Causes leakage of bacterial membrane. The hydrophobic tail is important in causing membrane damage suggesting a detergent-like mode of action.
 Source: semanticscholar.org
Source: semanticscholar.org
Polymyxin B works by breaking down the cytoplasmic membrane which generally results in bacterial cell death. Newton 1956 originally sug-gested that the mechanism. Mechanisms of polymyxin activity against Gram-negative bacteria resistance. Inhibits bacterial cell wall synthesis by preventing the incorporation of amino acids and nucleotides into the cell wall. Hydroxyl radical death mechanism in bacteria induced by polymyxin.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Polymyxin B was approved for medical use in the United States in 1964. Polymyxin B binds to phospholipids on cell membranes of gram-negative bacteria. Mechanisms of polymyxin activity against Gram-negative bacteria resistance. Polymyxin B was approved for medical use in the United States in 1964. Blocks production of tetrahydrofolic acid from dihydrofolic acid by binding to and reversibly inhibiting the enzyme dihydrofolate reductas.
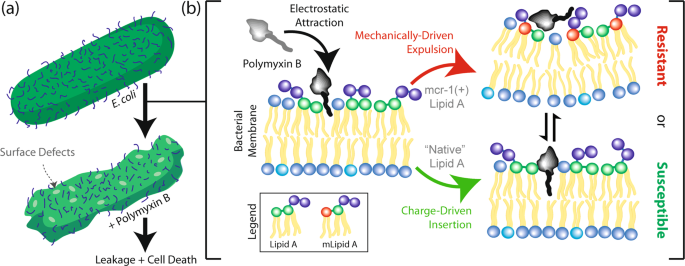 Source: nature.com
Source: nature.com
Polymyxin B is an antibiotic that disrupts the outer cell membrane of Gram negative bacteria binds and neutralizes lipopolysaccharide and inhibits respiration of Gram-negative bacterial cells 4. Polymyxin B binds to phospholipids in the gram-negative bacterial cell membrane. 19 The polycationic peptide ring binds to the outer membrane displacing the calcium. Polymyxin B sulfate trimethoprim is an antibiotic eye drop composed of two drugs. Proteus neisseria are resistant.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Mechanisms of polymyxin activity against Gram-negative bacteria resistance. Polymyxins are bactericidal with a time-dependent rate of killing at concentrations above their Minimal Bactericidal Concentration MBC. Even though the detailed mechanisms of polymyxin antibacterial activity are unknown their initial interaction with the lipid A of lipopolysaccharide is essential. Unfortunately very little has been achieved in the pharmaceutical industry to combat this problem. This binding destroys bacterial membranes with a surface detergent-like mechanism and increases the permeability of the cell membrane which results in loss of metabolites essential to bacterial existence.
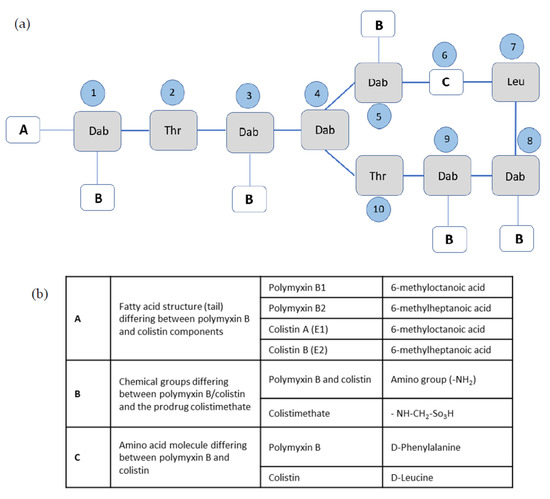 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
What is polymyxin btrimethoprim-ophthalmic and how does it work mechanism of action. The polymyxin molecule magenta comes across inner membrane IM and induces superoxide generation. Polymyxin B works by breaking down the cytoplasmic membrane which generally results in bacterial cell death. Polymyxin B is an antibiotic that disrupts the outer cell membrane of Gram negative bacteria binds and neutralizes lipopolysaccharide and inhibits respiration of Gram-negative bacterial cells 4. Polymyxin B can be given by a number of routes to treat susceptible Gram negative bacterial infections.
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site good, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title polymyxin mechanism of action by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






