Your Fosfomycin mechanism of action images are ready. Fosfomycin mechanism of action are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Find and Download the Fosfomycin mechanism of action files here. Download all free vectors.
If you’re looking for fosfomycin mechanism of action pictures information connected with to the fosfomycin mechanism of action interest, you have visit the right site. Our site always provides you with suggestions for refferencing the highest quality video and picture content, please kindly surf and find more informative video articles and graphics that fit your interests.
Fosfomycin Mechanism Of Action. Fosfomycin enters bacteria by utilizing the l-α-glycerophosphate transport system. Fosfomycin has a unique mechanism of action in which it irreversibly inhibits an early stage of bacterial cell wall biosynthesis. THE MECHANISM OF ACTION OF FOSFOMYCIN PHOSPHONOMYCIN Frederick M. Mechanism of action.
 Fosfomycin An Overview Sciencedirect Topics From sciencedirect.com
Fosfomycin An Overview Sciencedirect Topics From sciencedirect.com
Search for more papers by this author. This is the major route of entry. Fosfomycin acts in the bacterial cytoplasm inhibiting the cell wall biosynthesis in Gram-negative and -positive bacteria. Once inside the bacterium it acts as an analogue of phosphoenolpyruvate and irreversibly inhibits the enzyme pyruvyl transferase which catalyzes the. Covalently inhibits a cytoplasmic enzyme enolpyruvate transferase which blocks an early intracellular stage of cell wall synthesis Deck Winston 2012. Kahan Merck Institute for Therapeutic Research Rahway New Jersey 07065.
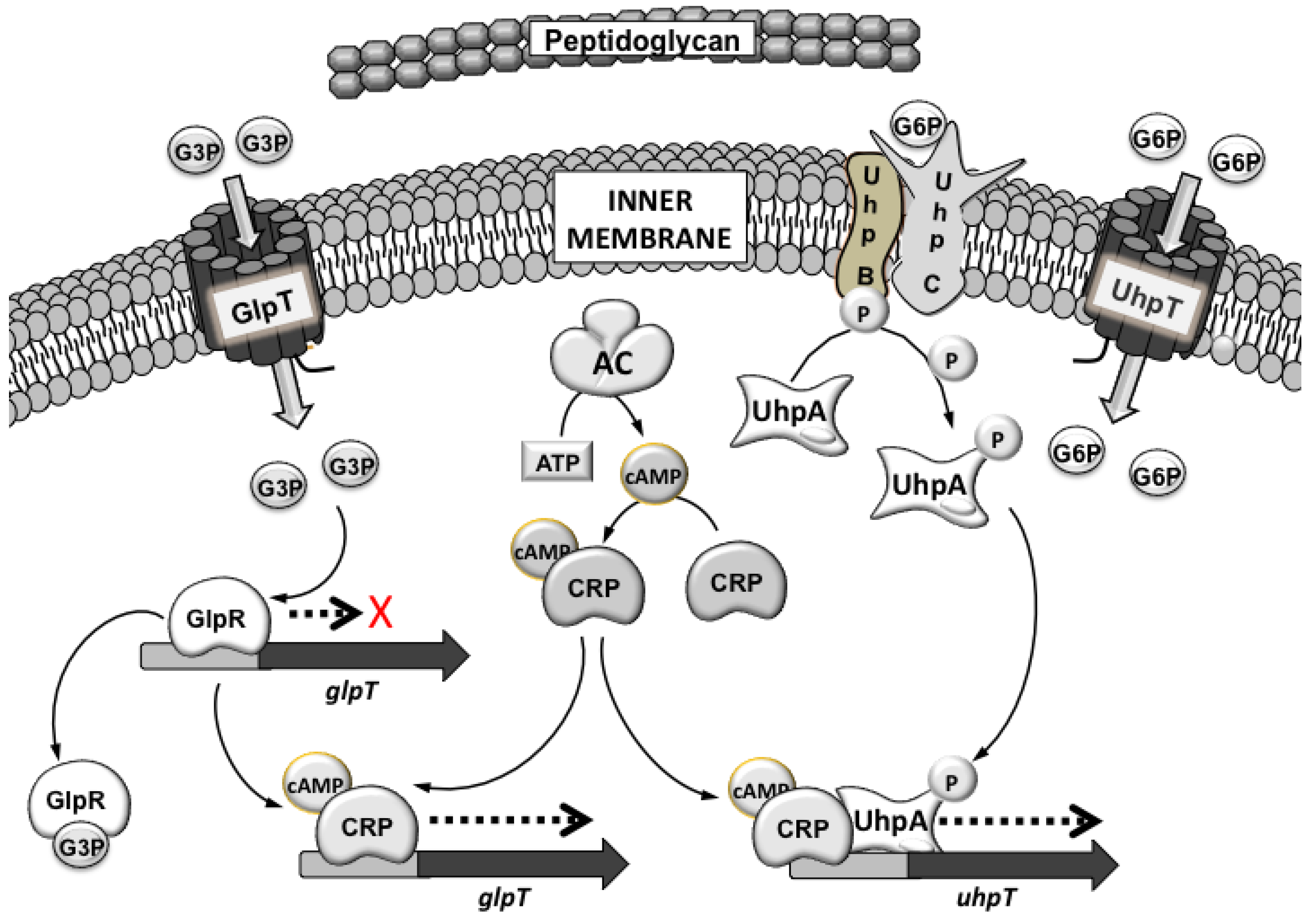
There is also a secondary transport system the hexose phosphate uptake system which can be induced by glucose-6-phosphate.
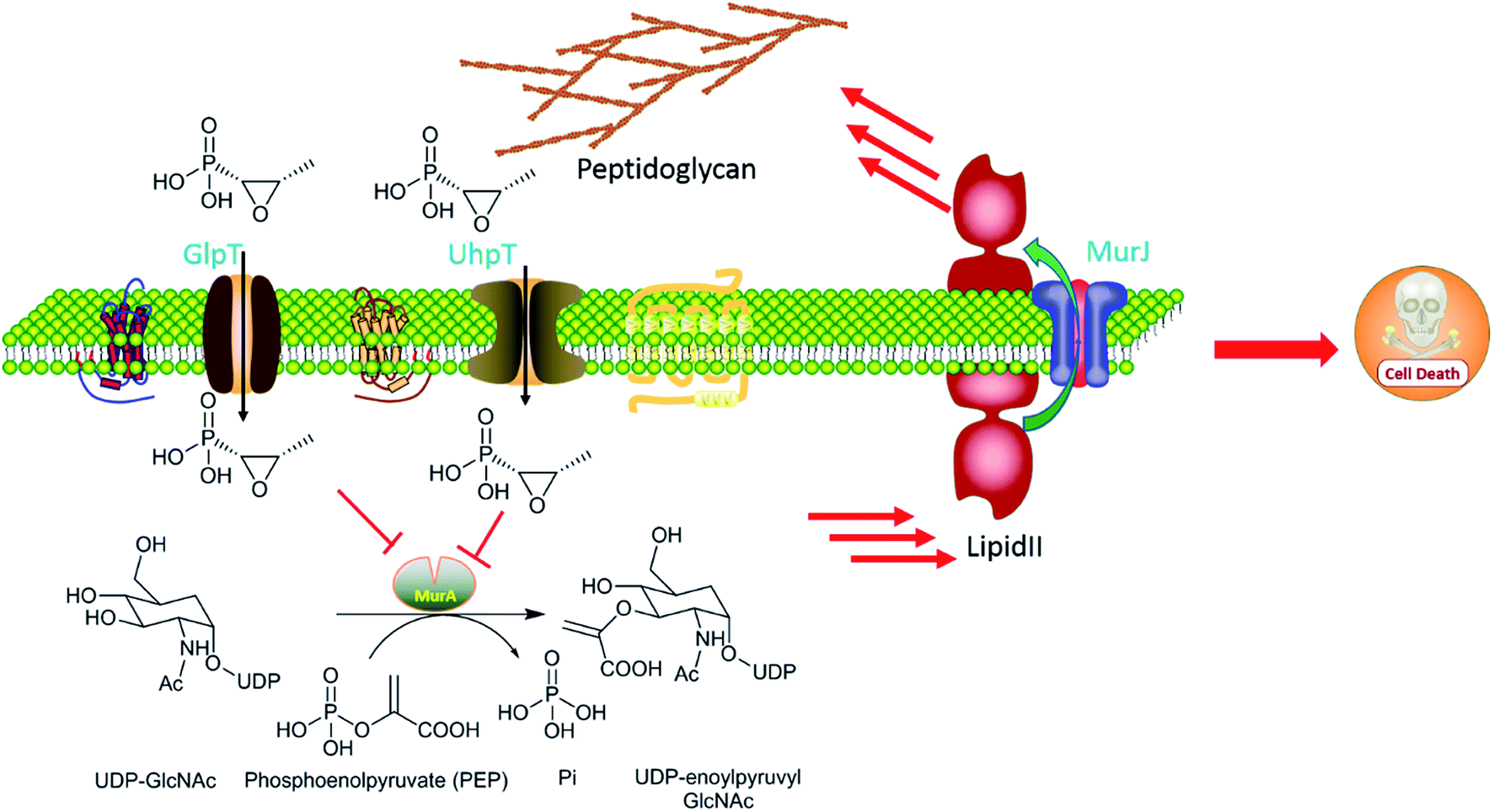
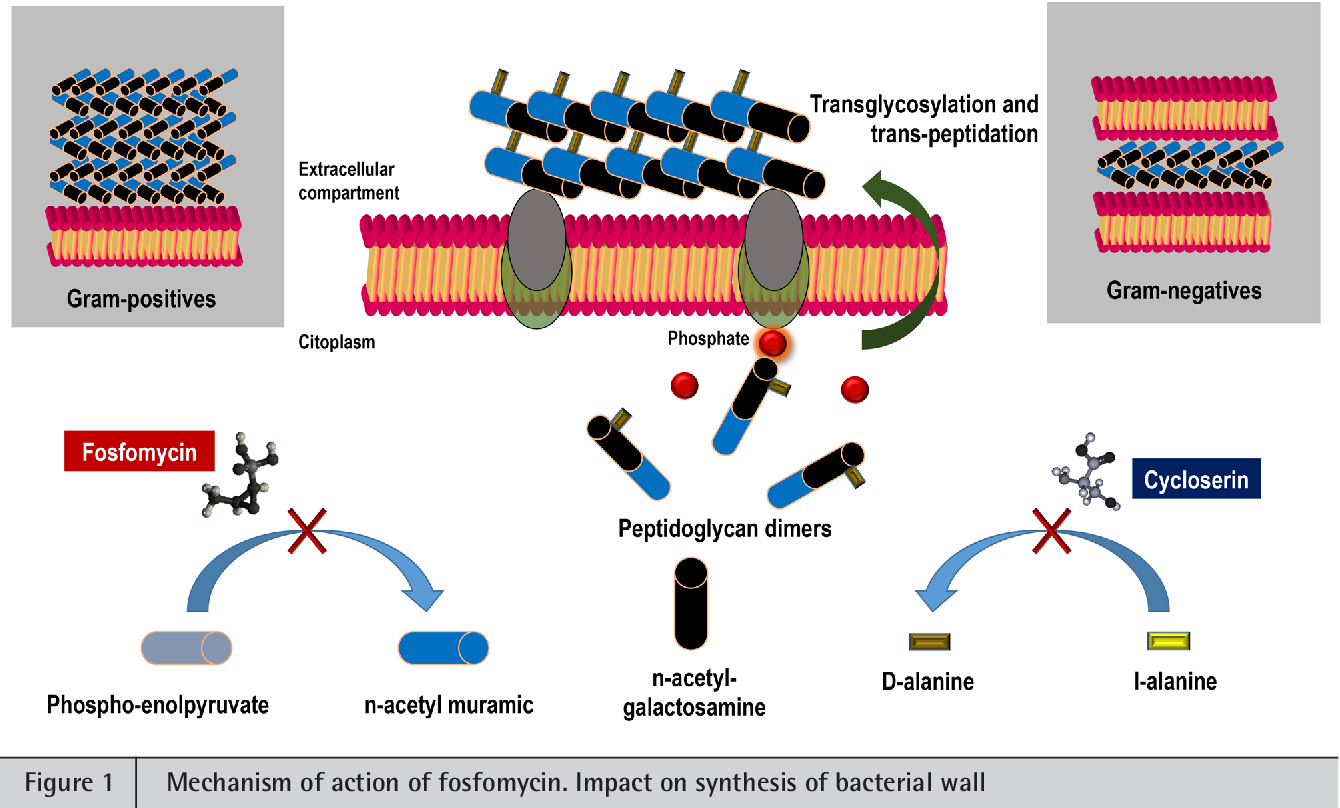
Mechanism of action. Fosfomycin is not cross-resistantwithotherantibioticsbecauseof its unique structureandmechanismofaction. Authors F M Kahan J S. Peptidoglycan is assembled from a building block composed of N-acetylglucosamine GlcNAc and N-acetylmuramic acid with an attached pentapeptide. Fosfomycin is a bactericidal antibiotic that inhibits the initial step in the biosynthesis of peptidoglycan in prokaryotes 5. The thiol function of the active site of pyruvate transferase reacts irreversibly with the epoxide of fosfomycin leading to an inactive enzyme.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
Mechanism of Action As a phosphonic acid derivative fosfomycin inhibits bacterial wall synthesis bactericidal by inactivating the enzyme pyruvyl transferase which is critical in the synthesis of cell walls by bacteria. Kahan Merck Institute for Therapeutic Research Rahway New Jersey 07065. The Mechanism of Action of Fosfomycin Phosphonomycin The Mechanism of Action of Fosfomycin Phosphonomycin The Mechanism of Action of Fosfomycin Phosphonomycin Ann N Y Acad Sci. Tyr343A residue on the other hand is only bound to catechin and quercetin. Mechanism of resistance.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
Staph aureus and gram-negative bacteria. REVIEW AND USE CRITERIA BACKGROUND Fosfomycin is a phosphonic acid derivative which inhibits peptidoglycan assembly thereby disrupting cell wall synthesis1 Its uptake into the bacterial cell occurs via active transport by the L-α-glycerophosphate transport and hexose phosphate uptake systems. Mechanism of action. A unique mechanism of action of fosfomycin made crossresistance to other antibiotic classes less common which motivated physicians to reevaluate its ability to destroy drug-resistant pathogens. This is the major route of entry.
 Source: jbc.org
Source: jbc.org
Mechanism of Action As a phosphonic acid derivative fosfomycin inhibits bacterial wall synthesis bactericidal by inactivating the enzyme pyruvyl transferase which is critical in the synthesis of cell walls by bacteria. The Mechanism of Action of Fosfomycin Phosphonomycin The Mechanism of Action of Fosfomycin Phosphonomycin The Mechanism of Action of Fosfomycin Phosphonomycin Ann N Y Acad Sci. Kahan Merck Institute for Therapeutic Research Rahway New Jersey 07065. Fosfomycin and ambuic acid have weak binding affinity as it is not bound to the residual His332A and Tyr343A. A unique mechanism of action of fosfomycin made crossresistance to other antibiotic classes less common which motivated physicians to reevaluate its ability to destroy drug-resistant pathogens.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Fosfomycin acts in the bacterial cytoplasm inhibiting the cell wall biosynthesis in Gram-negative and -positive bacteria. Specifically the initial reaction is the phosphorolysis of inosine and guanosine present in the meat extract portion of the media and the resultant f Kahan et al. Kahan Merck Institute for Therapeutic Research Rahway New Jersey 07065. The Mechanism of Action of Fosfomycin Phosphonomycin The Mechanism of Action of Fosfomycin Phosphonomycin The Mechanism of Action of Fosfomycin Phosphonomycin Ann N Y Acad Sci. Fosfomycin mimics phosphoenolpyruvate which is utilized by pyruvate transferase to synthesize UDP- N -acetyl muramic acid from UDP- N -acetyl glucosamine Figure 9.
 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
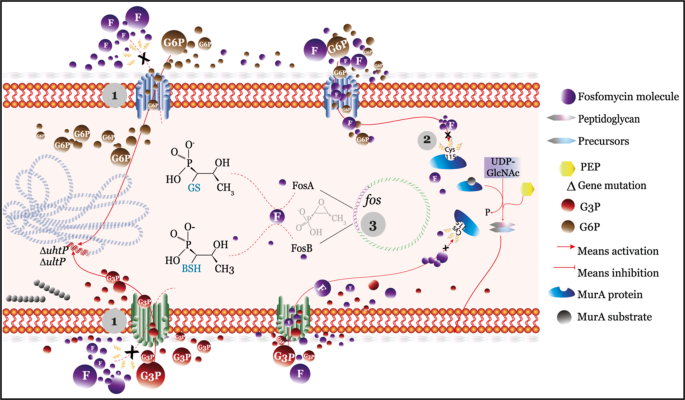
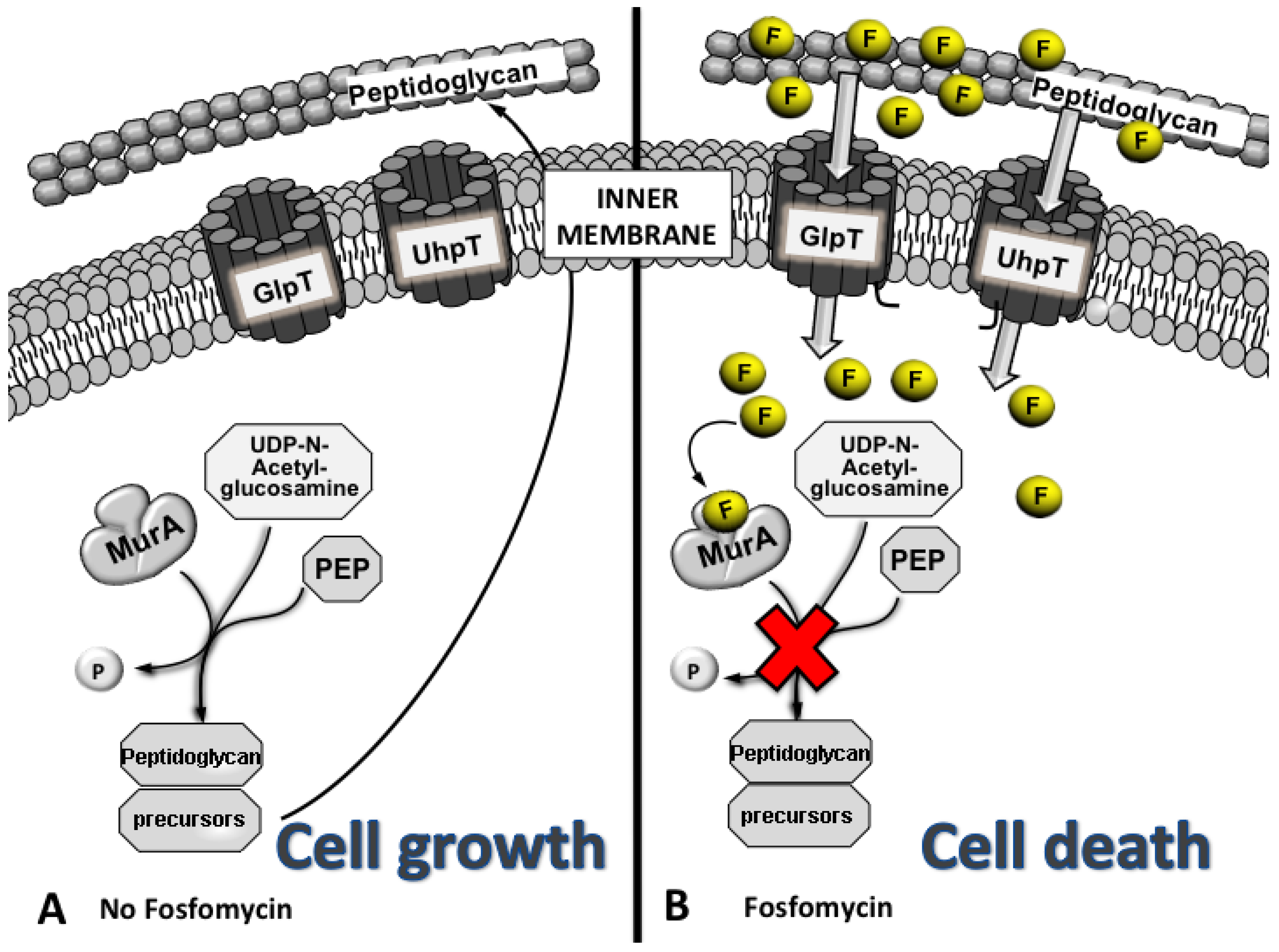
Fosfomycin enters the bacterium through membrane channelstransporters and inhibits MurA which initiates peptidoglycan PG biosynthesis of the bacterial cell wall. Fosfomycin has a unique mechanism of action in which it irreversibly inhibits an early stage of bacterial cell wall biosynthesis. Fosfomycin mimics phosphoenolpyruvate which is utilized by pyruvate transferase to synthesize UDP- N -acetyl muramic acid from UDP- N -acetyl glucosamine Figure 9. We are combating multi-drug resistance by introducing to the US. Reduced permeability mutation in chromosomal GlpT UhpT genes alters the transporter proteins responsible for uptake of fosfomycin Glycerol 3-phosphate transporter and glucose 6-phosphate transporter.

Fosfomycin has a unique mechanism of action in which it irreversibly inhibits an early stage of bacterial cell wall biosynthesis. A unique mechanism of action of fosfomycin made crossresistance to other antibiotic classes less common which motivated physicians to reevaluate its ability to destroy drug-resistant pathogens. Kahan Merck Institute for Therapeutic Research Rahway New Jersey 07065. Fosfomycin is an inhibitor of the MurA enzyme UDP-N-acetylglucosamine-enolpyruvyltransferase that catalyzes the first committed step in peptidoglycan synthesis the reaction of UDP-N-acetylglucosamine UDP-GlcNAc with phosphoenolpyruvate PEP to form UDP-GlcNAc-enoylpyruvate plus inorganic phosphate shown in Fig. Mechanism of Action As a phosphonic acid derivative fosfomycin inhibits bacterial wall synthesis bactericidal by inactivating the enzyme pyruvyl transferase which is critical in the synthesis of cell walls by bacteria.
 Source: pubs.rsc.org
Source: pubs.rsc.org
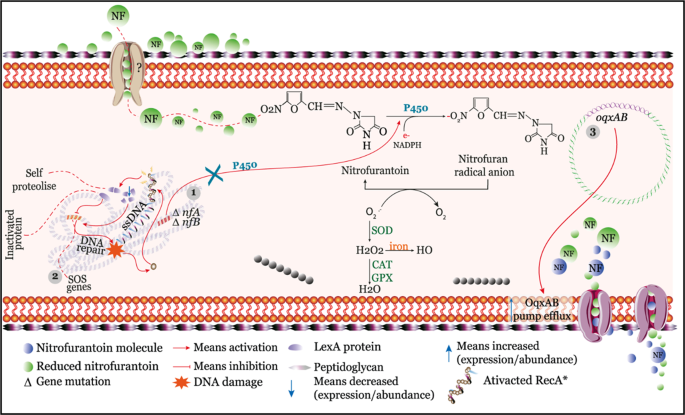
It inhibits bacterial cell wall synthesis through a unique mechanism of action at a step prior to that inhibited by β-lactams. Kahan Merck Institute for Therapeutic Research Rahway New Jersey 07065. Fosfomycin mimics phosphoenolpyruvate which is utilized by pyruvate transferase to synthesize UDP- N -acetyl muramic acid from UDP- N -acetyl glucosamine Figure 9. Fosfomycin Action Mechanism 381 ribose-1 -phosphate is converted to hexose phosphates by the seven enzymes of the pentose phosphate pathway. In order to exert its bactericidal activity fosfomycin must reach the bacterial cytoplasm.
 Source: nature.com
Source: nature.com
Fosfomycin is an inhibitor of the MurA enzyme UDP-N-acetylglucosamine-enolpyruvyltransferase that catalyzes the first committed step in peptidoglycan synthesis the reaction of UDP-N-acetylglucosamine UDP-GlcNAc with phosphoenolpyruvate PEP to form UDP-GlcNAc-enoylpyruvate plus inorganic phosphate shown in Fig. Kahan Merck Institute for Therapeutic Research Rahway New Jersey 07065. Specifically the initial reaction is the phosphorolysis of inosine and guanosine present in the meat extract portion of the media and the resultant f Kahan et al. Mechanism of resistance. Covalently inhibits a cytoplasmic enzyme enolpyruvate transferase which blocks an early intracellular stage of cell wall synthesis Deck Winston 2012.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
Peptidoglycan is assembled from a building block composed of N-acetylglucosamine GlcNAc and N-acetylmuramic acid with an attached pentapeptide. Tyr343A residue on the other hand is only bound to catechin and quercetin. Resistant to fosfomycin Falagas et al. Fosfomycin mimics phosphoenolpyruvate which is utilized by pyruvate transferase to synthesize UDP- N -acetyl muramic acid from UDP- N -acetyl glucosamine Figure 9. Transported into bacterial cells by glycerophosphate glucose-6-phosphate transport systems.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
A unique mechanism of action of fosfomycin made crossresistance to other antibiotic classes less common which motivated physicians to reevaluate its ability to destroy drug-resistant pathogens. Fosfomycin enters bacteria by utilizing the l-α-glycerophosphate transport system. Fosfomycin acts in the bacterial cytoplasm inhibiting the cell wall biosynthesis in Gram-negative and -positive bacteria. Specifically the initial reaction is the phosphorolysis of inosine and guanosine present in the meat extract portion of the media and the resultant f Kahan et al. THE MECHANISM OF ACTION OF FOSFOMYCIN PHOSPHONOMYCIN Frederick M.
 Source: nature.com
Source: nature.com
Reduced permeability mutation in chromosomal GlpT UhpT genes alters the transporter proteins responsible for uptake of fosfomycin Glycerol 3-phosphate transporter and glucose 6-phosphate transporter. This mechanism is seen in gram positives eg. Market an antibiotic with a new mechanism of action. Fosfomycin enters bacteria by utilizing the l-α-glycerophosphate transport system. This is the major route of entry.
 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
We are combating multi-drug resistance by introducing to the US. Tyr343A residue on the other hand is only bound to catechin and quercetin. Reduced permeability mutation in chromosomal GlpT UhpT genes alters the transporter proteins responsible for uptake of fosfomycin Glycerol 3-phosphate transporter and glucose 6-phosphate transporter. Fosfomycin is a bactericidal antibiotic that interferes with cell wall synthesis in both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria by inhibiting the initial step involving phosphoenolpyruvate synthetase. Kahan Merck Institute for Therapeutic Research Rahway New Jersey 07065.
 Source: semanticscholar.org
Source: semanticscholar.org
Kahan Merck Institute for Therapeutic Research Rahway New Jersey 07065. Fosfomycin and ambuic acid have weak binding affinity as it is not bound to the residual His332A and Tyr343A. It inhibits bacterial cell wall synthesis through a unique mechanism of action at a step prior to that inhibited by β-lactams. Mechanism of action. Mechanism of Action As a phosphonic acid derivative fosfomycin inhibits bacterial wall synthesis bactericidal by inactivating the enzyme pyruvyl transferase which is critical in the synthesis of cell walls by bacteria.

Market an antibiotic with a new mechanism of action. It inhibits bacterial cell wall synthesis through a unique mechanism of action at a step prior to that inhibited by β-lactams. Fosfomycin enters the bacterium through membrane channelstransporters and inhibits MurA which initiates peptidoglycan PG biosynthesis of the bacterial cell wall. Mechanism of resistance. CONTEPO previously referred to as ZOL.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Fosfomycin enters bacteria by utilizing the l-α-glycerophosphate transport system. Specifically the initial reaction is the phosphorolysis of inosine and guanosine present in the meat extract portion of the media and the resultant f Kahan et al. Fosfomycin is a bactericidal antibiotic that interferes with cell wall synthesis in both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria by inhibiting the initial step involving phosphoenolpyruvate synthetase. We are combating multi-drug resistance by introducing to the US. Fosfomycin enters bacteria by utilizing the l-α-glycerophosphate transport system.
 Source: semanticscholar.org
Source: semanticscholar.org
Fosfomycin enters bacteria by utilizing the l-α-glycerophosphate transport system. Covalently inhibits a cytoplasmic enzyme enolpyruvate transferase which blocks an early intracellular stage of cell wall synthesis Deck Winston 2012. This mechanism is seen in gram positives eg. MECHANISM OF ACTION FosfomycinisaninhibitoroftheMurAenzyme UDP-N-acetylglucosamine-enolpyruvyltrans-ferase thatcatalyzesthefirstcommittedstepin. Once inside the bacterium it acts as an analogue of phosphoenolpyruvate and irreversibly inhibits the enzyme pyruvyl transferase which catalyzes the.
 Source: semanticscholar.org
Source: semanticscholar.org
CONTEPO previously referred to as ZOL. The Mechanism of Action of Fosfomycin Phosphonomycin The Mechanism of Action of Fosfomycin Phosphonomycin The Mechanism of Action of Fosfomycin Phosphonomycin Ann N Y Acad Sci. THE MECHANISM OF ACTION OF FOSFOMYCIN PHOSPHONOMYCIN Frederick M. The Glu329A residue is bound to catechin fosfomycin and quercetin ligands. We are combating multi-drug resistance by introducing to the US.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
CONTEPO previously referred to as ZOL. There is also a secondary transport system the hexose phosphate uptake system which can be induced by glucose-6-phosphate. Transported into bacterial cells by glycerophosphate glucose-6-phosphate transport systems. Reduced permeability mutation in chromosomal GlpT UhpT genes alters the transporter proteins responsible for uptake of fosfomycin Glycerol 3-phosphate transporter and glucose 6-phosphate transporter. Tyr343A residue on the other hand is only bound to catechin and quercetin.
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site good, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title fosfomycin mechanism of action by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






