Your Denosumab mechanism of action images are ready. Denosumab mechanism of action are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Find and Download the Denosumab mechanism of action files here. Download all royalty-free vectors.
If you’re looking for denosumab mechanism of action images information connected with to the denosumab mechanism of action topic, you have pay a visit to the ideal blog. Our website frequently provides you with suggestions for viewing the maximum quality video and image content, please kindly surf and find more enlightening video articles and graphics that fit your interests.
Denosumab Mechanism Of Action. Review pharmacology about DENOSUMAB PROLIA. Denosumab acts by binding to and inhibiting RANKL leading to the loss of osteoclasts from bone surfaces. INDICATIONS XGEVA is indicated for. Bisphosphonates for example zoledronic acid bind to bone enter.
 Denosumab Mechanism Of Action And Clinical Outcomes Scienceopen From scienceopen.com
Denosumab Mechanism Of Action And Clinical Outcomes Scienceopen From scienceopen.com
Mechanism of Action Denosumab is a fully human immunoglobulin G2 monoclonal antibody with high affinity and specificity for human RANKL. Denosumab Femoral Neck BMD T-score -25 Overall Age 75 Boonen S McClung M et al. XGEVA is indicated for the prevention of skeletal-related events in patients with multiple myeloma and in patients with. Bone destruction in metastatic bone disease occurs mainly as a result of increased osteoclast activity stimulated by RANKL. Bone loss in giant cell tumours of. Visit the Official Product Website To View XGEVA Information.
Denosumab is the newest antiresorptive agent with a novel mechanism of action.
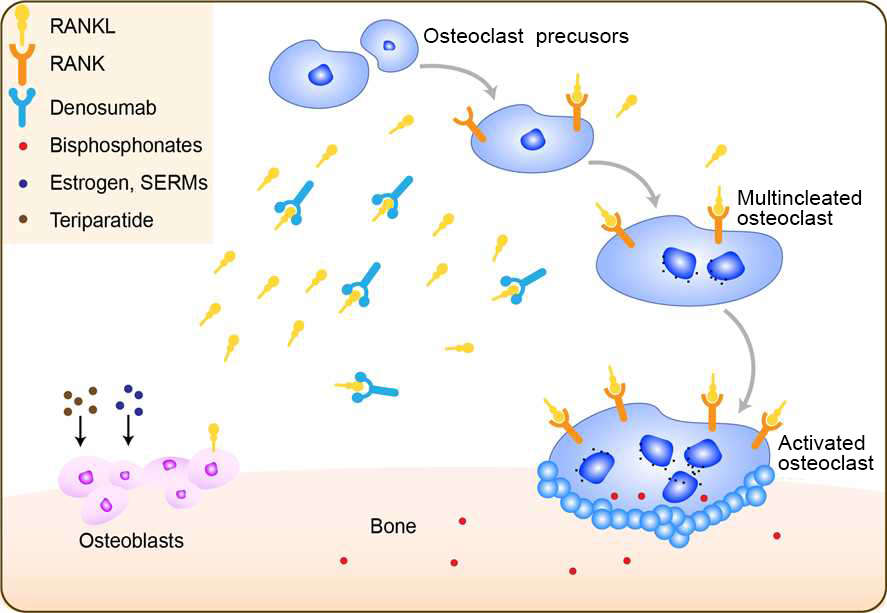
The discovery of RANKL and the essential role of RANK signaling in osteoclast differentiation activity and survival have led to the development of denosumab a fully human. Bone loss in giant cell tumours of. The discovery of RANKL and the essential role of RANK signaling in osteoclast differentiation activity and survival have led to the development of denosumab a fully human. Mechanism of Action of Denosumab Osteoporosis is a systemic skeletal disease that increases with age and is common among postmenopausal women. Identified by Osteoporosis Canada Clinical Practice Guidelines as a first-line agent for treatment. Briefly denosumab is a fully human monoclonal antibody that inhibits RANKL and helps regulate turnover in.
 Source: creativebiolabs.net
Source: creativebiolabs.net
6232015 2 Denosumab for osteoporosis - outline Mechanism of action Effect on fracture risk Effect on bone turnover and density Long-term effect on bone density Safety The characteristics of. Bone destruction in metastatic bone disease occurs mainly as a result of increased osteoclast activity stimulated by RANKL. Learn about the mechanism of disease in patients with solid tumors and find out how the XGEVA mechanism of action works to block the function of RANKL. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. Mechanism of Denosumab Denosumab is an antiresorptive agent that exists as a human IgG2 monoclonal antibody and inhibits the binding of the receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B ligand.
 Source: xgeva.com
Source: xgeva.com
6232015 2 Denosumab for osteoporosis - outline Mechanism of action Effect on fracture risk Effect on bone turnover and density Long-term effect on bone density Safety The characteristics of. Characterized by reduced bone. Prolia Mechanism of Action. XGEVA Mechanism of Action XGEVA denosumab for HCPs. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
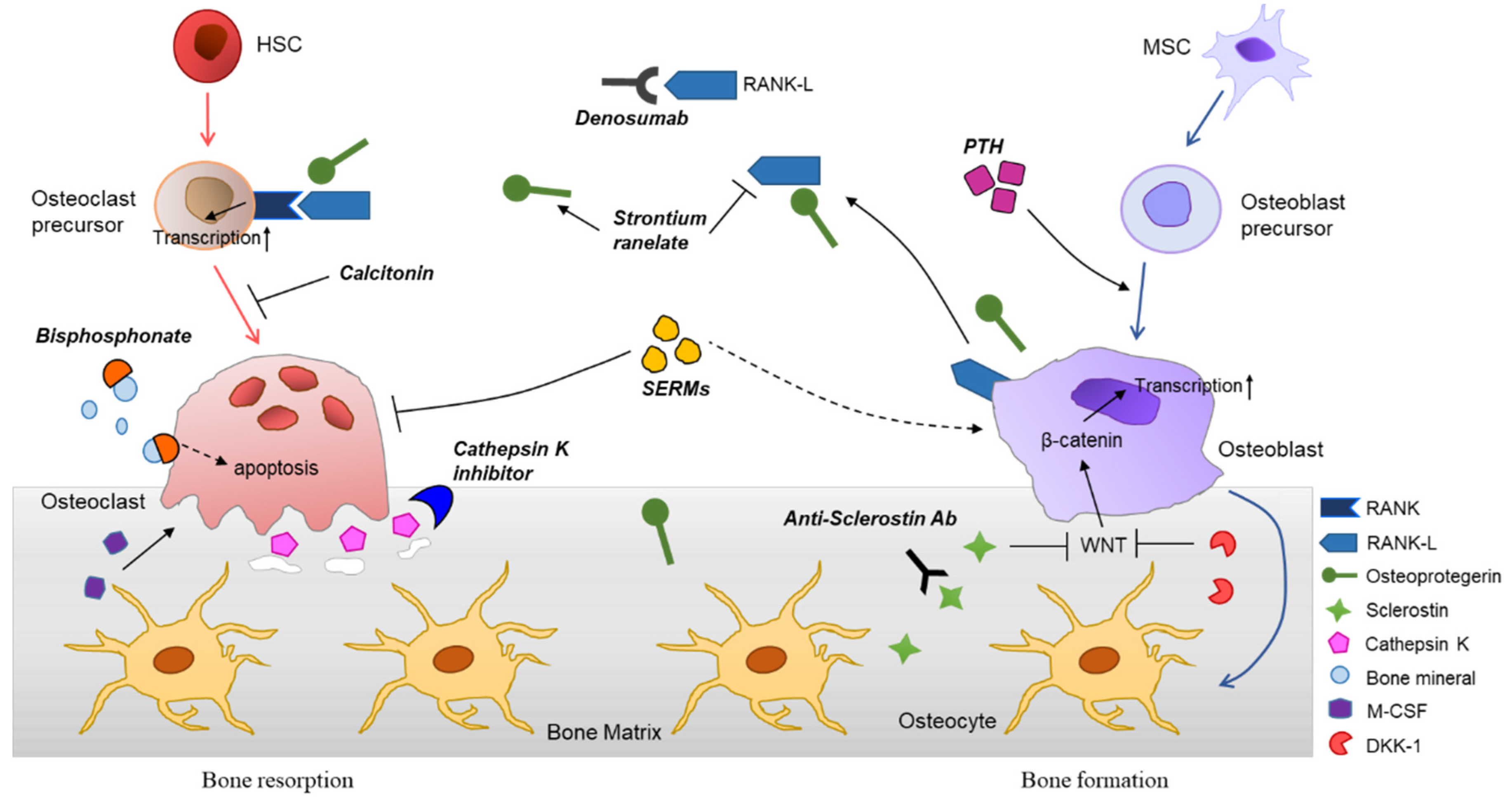
Learn about the mechanism of disease in patients with solid tumors and find out how the XGEVA mechanism of action works to block the function of RANKL. Mechanism of action differences are not meant. Bisphosphonates oestrogen denosumab reduce bone turnover by distinct mechanisms. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. Denosumab a recently approved therapy is a fully human monoclonal antibody that.
 Source: clinicaltherapeutics.com
Source: clinicaltherapeutics.com
Review pharmacology about DENOSUMAB PROLIA. Denosumab acts by a novel mechanism and is administered twice yearly by subcutaneous injection. Characterized by reduced bone. Learn about the mechanism of disease in patients with solid tumors and find out how the XGEVA mechanism of action works to block the function of RANKL. XGEVA denosumab mechanism of action.
 Source: scienceopen.com
Source: scienceopen.com
Visit the Official Product Website To View XGEVA Information. Briefly denosumab is a fully human monoclonal antibody that inhibits RANKL and helps regulate turnover in. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. Denosumab prevents RANKL from. The discovery of RANKL and the essential role of RANK signaling in osteoclast differentiation activity and survival have led to the development of denosumab a fully human.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Side effects uses dose INJECTION warnings precautions benefits indications mechanism of action MOA. Bone destruction in metastatic bone disease occurs mainly as a result of increased osteoclast activity stimulated by RANKL. Denosumab acts by a novel mechanism and is administered twice yearly by subcutaneous injection. Mechanism of action differences are not meant. By binding to RANKL denosumab inhibits.
 Source: xgeva.com
Source: xgeva.com
Denosumab acts by binding to and inhibiting RANKL leading to the loss of osteoclasts from bone surfaces. Denosumab is the newest antiresorptive agent with a novel mechanism of action. XGEVA Mechanism of Action XGEVA denosumab for HCPs. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. Learn about the mechanism of disease in patients with solid tumors and find out how the XGEVA mechanism of action works to block the function of RANKL.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Bisphosphonates for example zoledronic acid bind to bone enter. Denosumab acts by binding to and inhibiting RANKL leading to the loss of osteoclasts from bone surfaces. Bone destruction in metastatic bone disease occurs mainly as a result of increased osteoclast activity stimulated by RANKL. Denosumab Femoral Neck BMD T-score -25 Overall Age 75 Boonen S McClung M et al. Mechanism of Action of Denosumab Osteoporosis is a systemic skeletal disease that increases with age and is common among postmenopausal women.
 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
XGEVA Mechanism of Action XGEVA denosumab for HCPs. Denosumab Femoral Neck BMD T-score -25 Overall Age 75 Boonen S McClung M et al. Visit the Official Product Website To View XGEVA Information. Prolia is an antiresorptive RANK Ligand inhibitor and its mechanism of action makes it different than a bisphosphonate. Side effects uses dose INJECTION warnings precautions benefits indications mechanism of action MOA.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Mechanism of Action of Denosumab Osteoporosis is a systemic skeletal disease that increases with age and is common among postmenopausal women. Mechanism of Action of Denosumab Osteoporosis is a systemic skeletal disease that increases with age and is common among postmenopausal women. Denosumab acts by a novel mechanism and is administered twice yearly by subcutaneous injection. XGEVA Mechanism of Action XGEVA denosumab for HCPs. 6232015 2 Denosumab for osteoporosis - outline Mechanism of action Effect on fracture risk Effect on bone turnover and density Long-term effect on bone density Safety The characteristics of.

By binding to RANKL denosumab inhibits. The discovery of RANKL and the essential role of RANK signaling in osteoclast differentiation activity and survival have led to the development of denosumab a fully human. In phase 3 clinical studies denosumab was shown to significantly reduce vertebral. XGEVA Mechanism of Action XGEVA denosumab for HCPs. Learn about the mechanism of disease in patients with solid tumors and find out how the XGEVA mechanism of action works to block the function of RANKL.
 Source: europepmc.org
Source: europepmc.org
In phase 3 clinical studies denosumab was shown to significantly reduce vertebral. Review pharmacology about DENOSUMAB PROLIA. In phase 3 clinical studies denosumab was shown to significantly reduce vertebral. Mechanism of Action of Denosumab Osteoporosis is a systemic skeletal disease that increases with age and is common among postmenopausal women. Visit the Official Product Website To View XGEVA Information.
 Source: xgeva.com
Source: xgeva.com
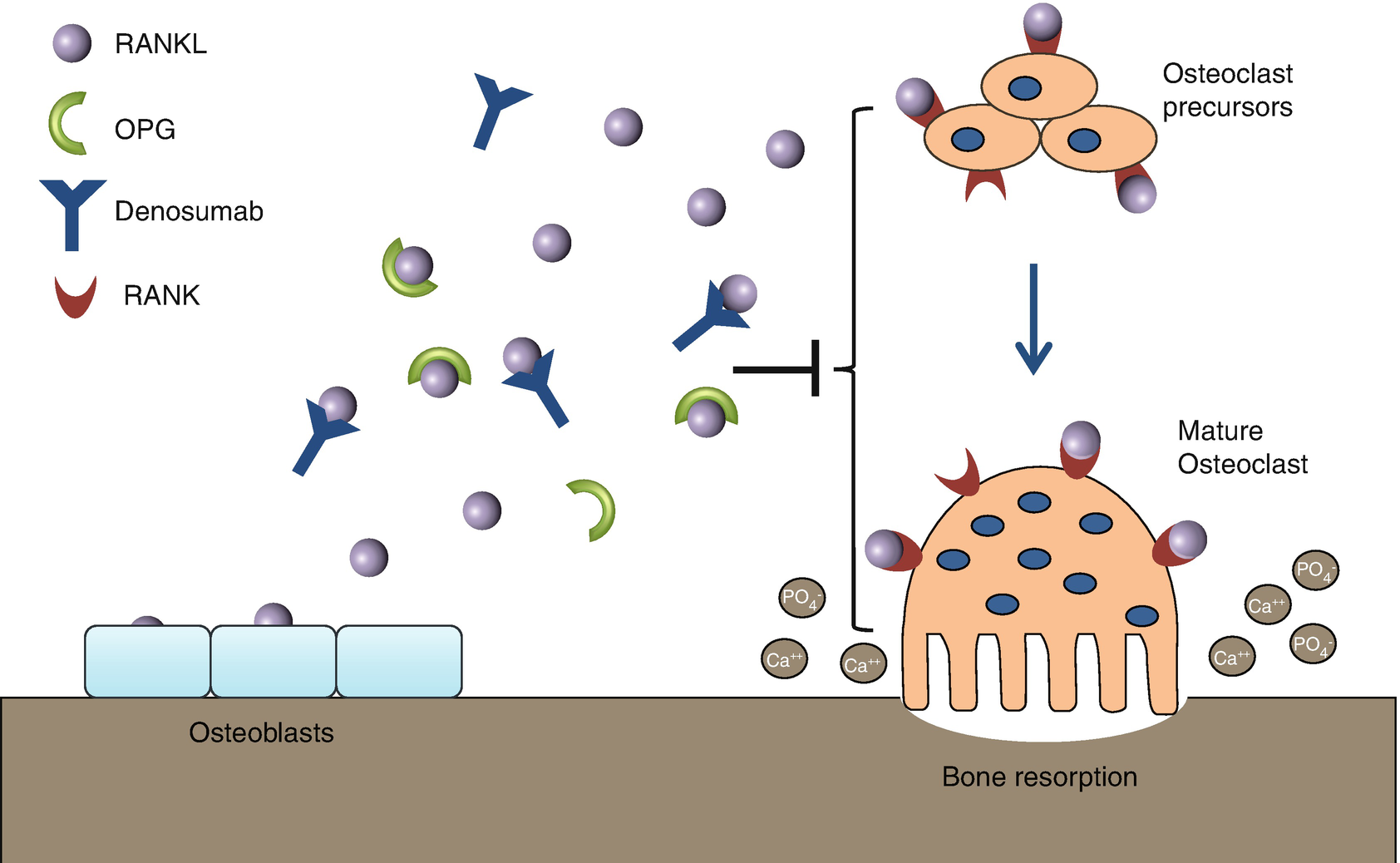
Denosumab is a fully human monoclonal antibody that binds to RANKL and thereby inhibits the activation of osteoclasts by RANKL. Characterized by reduced bone. Review pharmacology about DENOSUMAB PROLIA. Denosumab is a human monoclonal antibody that binds to the human RANK ligand RANKL on the surface of osteoclasts and their precursors. 6232015 2 Denosumab for osteoporosis - outline Mechanism of action Effect on fracture risk Effect on bone turnover and density Long-term effect on bone density Safety The characteristics of.
 Source: link.springer.com
Source: link.springer.com
Visit the Official Product Website To View XGEVA Information. Prolia Mechanism of Action. Characterized by reduced bone. Outline Mechanism of action Effect on fracture risk. By binding to RANKL denosumab inhibits.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
By binding to RANKL denosumab inhibits. By binding to RANKL denosumab inhibits. Review pharmacology about DENOSUMAB PROLIA. Visit the Official Product Website To View XGEVA Information. Bisphosphonates oestrogen denosumab reduce bone turnover by distinct mechanisms.
 Source: europepmc.org
Source: europepmc.org
Identified by Osteoporosis Canada Clinical Practice Guidelines as a first-line agent for treatment. XGEVA is indicated for the prevention of skeletal-related events in patients with multiple myeloma and in patients with. XGEVA denosumab mechanism of action. Denosumab acts by binding to and inhibiting RANKL leading to the loss of osteoclasts from bone surfaces. Denosumab acts by a novel mechanism and is administered twice yearly by subcutaneous injection.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Outline Mechanism of action Effect on fracture risk. Mechanism of Denosumab Denosumab is an antiresorptive agent that exists as a human IgG2 monoclonal antibody and inhibits the binding of the receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B ligand. Side effects uses dose INJECTION warnings precautions benefits indications mechanism of action MOA. Prolia Mechanism of Action. By binding to RANKL denosumab inhibits.

Denosumab Femoral Neck BMD T-score -25 Overall Age 75 Boonen S McClung M et al. Visit the Official Product Website To View XGEVA Information. XGEVA Mechanism of Action XGEVA denosumab for HCPs. Mechanism of Denosumab Denosumab is an antiresorptive agent that exists as a human IgG2 monoclonal antibody and inhibits the binding of the receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B ligand. In phase 3 clinical studies denosumab was shown to significantly reduce vertebral.
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site convienient, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title denosumab mechanism of action by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






